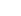Exosomes have gained global traction in aesthetic and regenerative medicine space in recent years. Beauty brands and clinics are now embracing exosome-based technology and expanding their offerings. Beyond another ingredient on a label, the nourishing properties of exosomes are highly sought after— yet the quality and efficacy may vary depending on the manufacturing process.
This article explains the basics and key technologies used in exosome manufacturing process, and familiarize readers with the importance of each step to exosome product quality.
Exosome Manufacturing Process: The Tech
The exosome manufacturing process consists of several major processes: cell culture, exosome collection, purification, and filling/packaging for storage or delivery. Each individual step is interconnected from upstream to downstream, as failure in any point can compromise the quality and safety of the final product.
4 key Technologies used in the process:
-
Rapid Cell Expansion
Exosomes come from living cells. Keeping the cells healthy and getting the quantity up are keys to efficient exosome production.
-
AIoT-Based Process Monitoring
Automated systems provide real-time monitoring of the process 24/7. Smart technologies help minimizes human error and ensure consistency.
-
Aseptic Process & Regulatory Compliance
Aseptic process ensures product safety from start to finish. Implementing global standards (e.g., PIC/S GMP) is essential for commercialization.
-
Freeze-Drying and Aseptic Filling
Freeze-dried exosomes have greatly extended shelf-life, and allow room temperature storage and shipping.
1. Rapid Cell Expansion — The Basis of Exosome Production
The Cells are Growing Fast. But Why We Need the Cells in Top Condition?
Exosomes are tiny vesicles secreted by living cells. The condition of the cells directly affects the quality and functionality of secreted exosomes. When cells are metabolically active and healthy, they tend to consistently produce functionally potent exosomes with more bioactive substances. In contrast, stressed or aging cells may generate vesicles with low potency or inconsistent properties.
Rapid and stable cell expansion is particularly critical for commercial applications, where batch-to-batch consistency is key. When cells grow under carefully managed conditions, we can make sure every production run meets the quality standards, with reduced variability and downstream risks.
What Technologies Are Used in Cell Expansion?
In exosome manufacturing, cell expansion is commonly done using these two technologies:
-
Multilayer Flasks (e.g., CellSTACK)
Ideal for early-stage research and small-to-medium scale production. Provides ample surface area for cell expansion.
-
Bioreactors
Support automated, large-scale cell culture. Indispensable for massive commercial production.
In some facilities, advanced automated culture system and process analytics are implemented to boost productivity and minimize contamination. Such systems are connected to AIoT monitoring platform to allow AI-assisted seamless supervision of the whole operation.
2. Smarter Exosome Manufacturing Process: How AIoT Helps Get the Job Done.
Exosome Production and AIoT? What about it?
AIoT — the combination of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) — is transforming how we control exosome manufacturing processes. Think of it as a tireless supervisor meticulously watching over every move of the entire production line.
Traditional process mostly relies on human supervision and intervention on site, which creates information gaps, human errors, and environmental risk. By implementing AIoT technology, we can track critical parameters in real time, including temperature, pH, gas composition, and pressure change. The system will alert the operators when anomalies are identified, and take care of the problem proactively, to ensure operational performance and product safety.
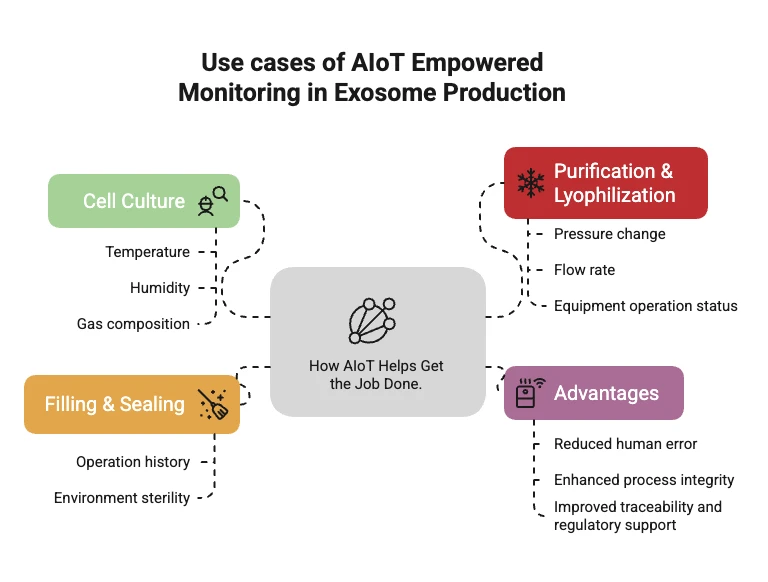
What Parameters Can AIoT Monitor in Exosome Manufacturing?
AIoT platforms can cover the entire exosome manufacturing workflow, including:
- Cell Culture: Monitoring temperature, humidity, gas composition, and media change frequency.
- Purification and Freeze-Drying: Tracking pressure changes, flow rates, and equipment performance.
- Filling and Packaging: Logging operator actions and environmental cleanliness levels.
All data is captured and stored at a centralized database, establishing complete audit trails for regulatory inspections or internal audits.
What Are the Advantages of AIoT Integration?
For manufacturers of exosome products, adopting AIoT offers three key advantages:
- Reduced Human Error: Lower risk of contamination or operational mistakes through automated oversight.
- Enhanced Process Integrity: Every batch is produced under consistent, validated conditions.
- Traceability and Compliance: Complete digital records provide support for audits and regulatory approvals.
Globally, regulatory requirements are becoming more stringent over time. As clients begin to demand supply transparency, AIoT-powered audit trail and chain-of-custody will be the next industry standard in exosome manufacturing.
3. How Should Exosome Manufacturing Process Comply with Global GMP Standard?

What Is PIC/S GMP? Is It Required for Exosome Facilities?
PIC/S GMP refers to internationally harmonized Good Manufacturing Practice developed by the Pharmaceutical Inspection Co-operation Scheme (PIC/S) to ensure product quality and safety.
While originally developed for pharmaceutical production, these guidelines are now adopted for regenerative medicine, including cell therapy and exosome-based products.
If the manufacturer’s goal is to access global markets, starting clinical trials, or marketing exosomes as cosmetic ingredients, GMP-compliant facilities is a must. Failing to comply could create legal and regulatory challenges during product commercialization and limitations in sales.
📚 Reference: ScienceDirect - GMP Challenges for Exosomes
Which Process Stage Carries High Contamination Risk — and What Can be Done?
Several stages in the exosome manufacturing process are particularly prone to contamination:
-
Post-purification concentrate
The concentrate risks exposure to contaminants before they are properly stored in closed vessels, thus making this step highly risky.
-
Freeze-drying and filling
This step involves prolonged handling time, and carries substantial risk of introducing airborne contaminants.
-
Pre-storage handling and transfer
Operating without closed system could increase exposure to environmental contaminants.
Key facility design for contamination risk mitigation:
-
Operation in closed Isolator systems
Isolated Class A aseptic environment that limits exposure.
-
Using H₂O₂ sterilization and RTP (Rapid Transfer Ports)
Prevent raw materials and containers from being exposed to unfiltered air.
-
Separate personnel and material route
Minimizes cross-contamination during production.
What’s New in the Updated GMP Guidelines — and What should Manufacturers Plan Accordingly?
As of 2023, PIC/S GMP update enforces Contamination Control Strategies (CCS) as a core requirement. For exosome manufacturers, key changes include:
- Increased sterilization and validation frequency of freeze-drying equipment
- Mandatory Media Fill Tests for aseptic filling simulations
- More comprehensive documentation of personnel actions, equipment performance, environmental conditions, and deviations
4. Why Aseptic Lyophilization Is Crucial for Exosome Storage— and What You Need to Know
Why Use Lyophilization? Can Exosomes Be Stored Without Freeze-Drying?
Exosomes, like most biological substances, are temperature sensitive. Without proper cold storage, exosomes would suffer bioactivity loss at room temperature, or even under refrigeration. Lyophilization (freeze-drying) emerged as a great solution and become the current gold standard for exosome storage.
Freeze-drying turns exosomes into a stable powder form, making storage and transport easier while providing product stability and flexibility (e.g., reconstituting into essence or injectables).
Exosomes in liquid have much shorter shelf lives, stringent storage requirements, and high risk of degradation during shipping.
How to Maintain Sterility During Freeze-Drying? What Equipment Is Required?
Standard freeze-dryers do not operate under aseptic conditions. To keep contamination at bay, the entire process should operate in aseptic environment, such as in an isolator. Common market solutions include:
-
Isolators
Isolators fully seal off the freeze-dryer and filling line within a Class A aseptic environment.
-
Integrated H₂O₂ Sterilization and RTP Ports
Containers, stoppers, and materials are sterilized before entering the isolator system, eliminating exposure to airborne contaminant.
-
Automated Filling Line
Reduce manual operation and lower the contamination risk during the final steps.
This setup ensures complete aseptic freeze-drying and compliance with international pharmaceutical standards for aseptic filling.
What’s changed in PIC/S GMP 2023 Update About Freeze-Drying Processes?
Under the revised 2023 PIC/S GMP guidelines, lyophilization has become a focal point in Contamination Control Strategies (CCS). Here are the key compliance requirements:
-
Full Equipment Validation (DQ/IQ/OQ/PQ)
Ensures the freeze-dryer is designed, installed, operated, and performing within regulatory expectations.
-
Annual Media Fill Tests
Simulates entire filling process to validate sterility under real-world conditions.
-
Traceable Recordkeeping and Data Logging
Includes environmental monitoring, sterilization logs, and batch identification for comprehensive site audit.
For exosome manufacturers, lyophilization is not a gimmick — it is now a necessity and competitive edge in global market.
Winning the Exosome Arm Race with These 4 Core Manufacturing Technologies
Producing high-quality exosome product takes more than sourcing good raw materials — it also requires a robust manufacturing process.
Rapid cell expansion, AIoT-powered real-time process monitoring and control, PIC/S GMP-compliant aseptic operations, and sterile lyophilization to allow reliable product storage and transport — these four pillars form the backbone of our exosome product.
For those planning to build a facility, outsource manufacturing, or just to evaluate supplier capabilities, understanding these technologies will help you make smarter decisions and the competition landscape.
Safeguard quality from the Start: YJ-Bio’s End-to-End Expertise
This article showcases how high quality and sterile exosomes are manufactured.
Quality has always been the core value of our end-to-end process because product safety and efficacy depend on the integrity of every step.
We offer comprehensive planning and services, including:
- Cleanroom layout design and consulting
- Isolator-based cell processing workflow integration
- DQ/IQ/OQ/PQ validation & VHP sterilization
- Tech transfer and SOP implementation
Planning and building a GMP-compliant, safe, and scalable production line — from scratch.
🧪 YJ-Isolator: A GMP-compliant Workstation for Cell & EV Production
Purpose-built for cell and exosome manufacturing, our YJ-Isolator integrates:
- Cell Incubator
- Microscope/Display
- Centrifuge
Customization available to accommodate client’s unique process on our ready-to-use isolator platform.
- Human umbilical cord-derived Exosomes (spec: 50 billion / 300 billion vesicles)
- Immune and stem cell culture services for R&D and product development
Let us take care of the raw material production and risks, so you can focus 100% on delivering better products.
Further Reading & References
-
Manufacturing Therapeutic Exosomes: From Bench to Industry
Overview of exosome manufacturing workflows and GMP implementation challenges.
-
Strategies and Technologies for GMP-Scale Exosome Isolation
In-depth look at purification methods and scale-up requirements.
-
Freeze‑Dried Extracellular Vesicles from Adipose-Derived Cells
Research on freeze-drying techniques and excipient selection for EV preservation.
-
Clinical Application Guidance for Extracellular Vesicles
Focuses on aseptic processing and contamination control for clinical-grade EVs.
-
Exosomes Produced in Bioreactors
Case study highlighting bioreactor-based scale-up solutions.
-
Taiwanese News Feature on Exosome Quality & Storage Standards
Industry experts discuss purity and the importance of sterile lyophilization for long-term stability.